Vol.43,No.3,2016
| |
|
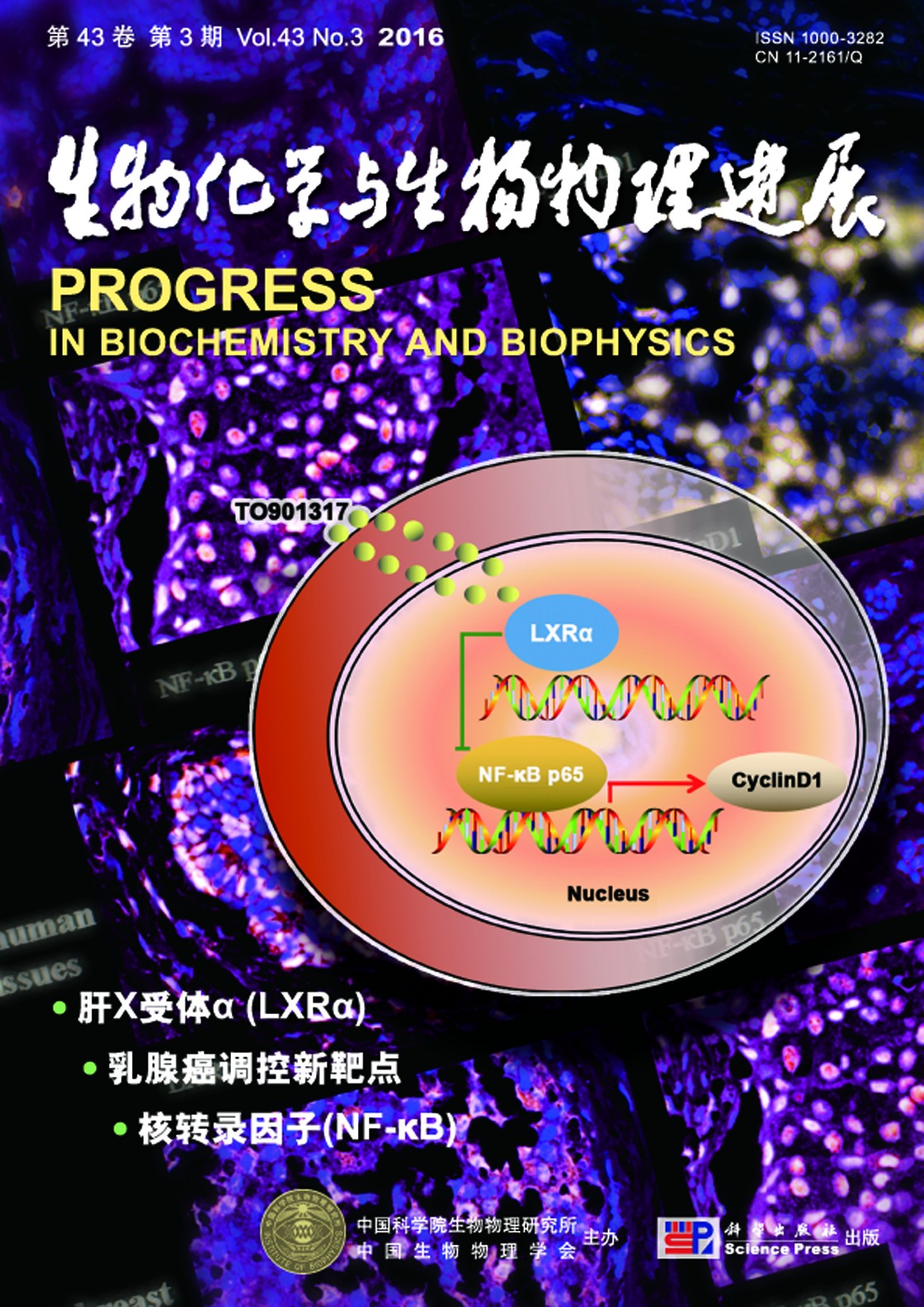
Cover Story:LXRα could have the anti-proliferative effect on multiple cancer cells including breast cancer. However, the mechanisms of LXRα regulating the breast cancer cells remain unclear. This study is to investigate the different expression of LXRα, NF-κB p65 and cyclinD1 in the proliferation of human breast cancer cells. At first, LXRα, NF-κB p65 and cyclinD1 expression were detected by immunohistochemical staining in human breast cancer and paired adjacent breast tissues (n=60). As a result, the three kinds of protein were mainly expressed in cell nuclei. Among them, NF-κB p65 and cyclinD1 were higher expressed in breast cancer tissues than in adjacent tissues while LXRα was lower expressed. Then, MTT assay was used to detect the proliferation of MCF-7 cells and Western blot was used to examine the expression of the three kinds of protein. TO901317 (a kind of artificial agonists against LXRs especially for LXRα) could increase LXRα expression, but decrease NF-κB p65 and cyclinD1 expression and suppress the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner (P < 0.05). Finally, the effects of LXRα siRNA and pyrrolidinedithiocarbamic acid (PDTC, an inhibitory of NF-κB) on TO901317 were observed respectively. LXRα siRNA could significantly decrease the up-regulation of LXRα expression and reverse the inhibited effect of TO901317 on cyclinD1 and NF-κB p65 expression and MCF-7 cell proliferation (P < 0.05) while PDTC could strengthen the inhibition of cell proliferation and further down-regulate NF-κB p65 and cyclinD1 expression induced by TO901317 (P < 0.05), but have little effect on LXRα. In a conclusion, the expression of LXRα, NF-κB p65 and cyclinD1 plays an important role in the proliferation of human breast cancer cells, so as to provide a new method for the molecular targeting treatment of breast cancer in the future.
|
Reviews and Monographs
Research Papers
Techniques and Methods
|
|
