2023年第50卷第7期目录
| |
|
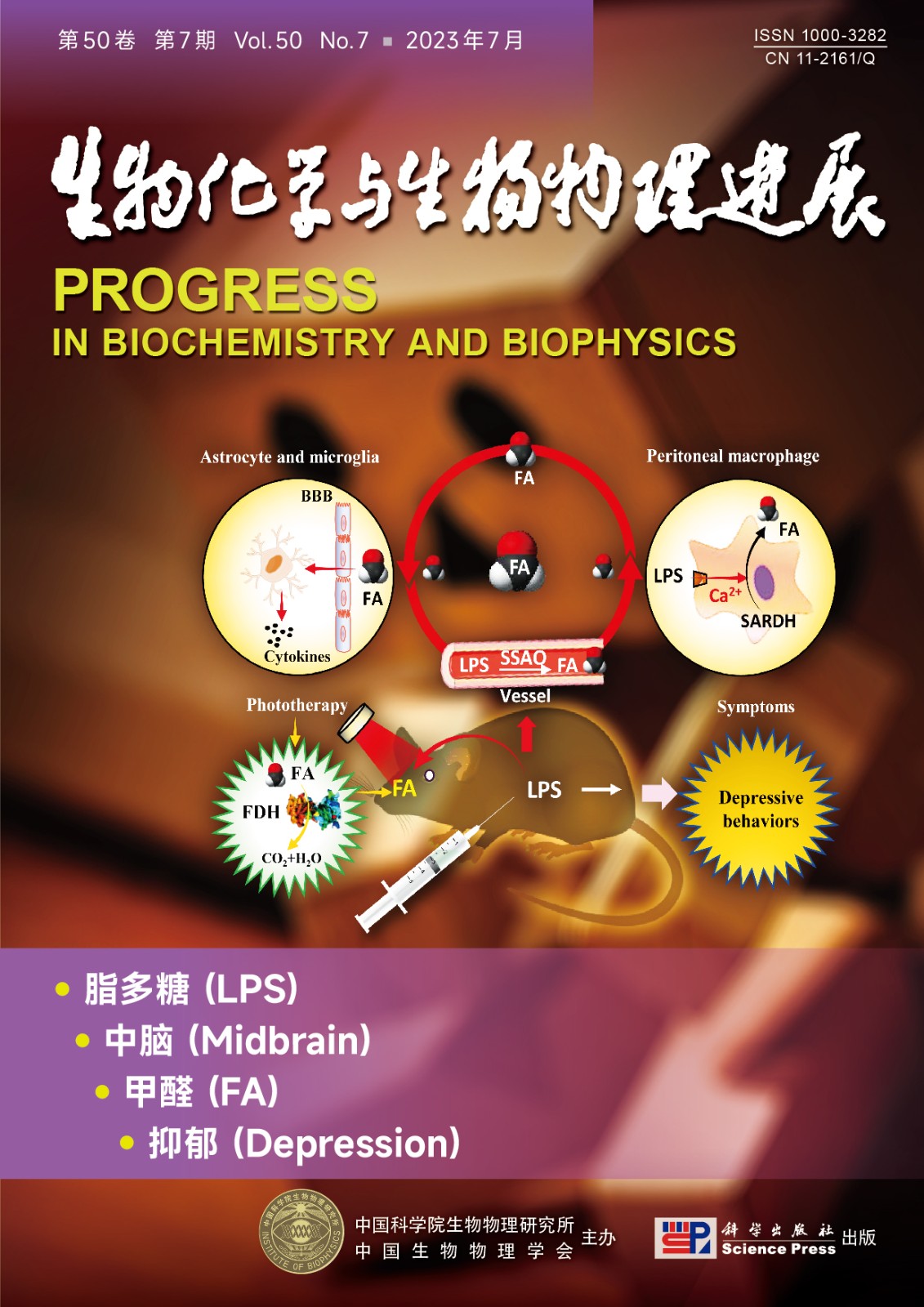
封面故事:抑郁的发生机制不清及药物临床疗效不佳是世界难题。外周腹腔注射脂多糖
(lipopolysaccharide,LPS) 常常用来模拟临床抑郁症状,而外周LPS如何诱发脑部病变并出现抑郁
行为的机制不明。赵丹睿等发现,外周LPS注射可通过激活小鼠的血液氨基脲敏感胺氧化酶(SSAO)
而产生内源甲醛(FA),也可激活腹腔巨噬细胞产生甲醛。LPS很难穿透血脑屏障(BBB) 进
入脑部。但是小分子的甲醛可随血液循环到中脑(midbrain) 并蓄积,激活中脑胶质细胞(microglia)
产生炎症因子,如:IL-1β、TNF-α、IL-6。而这些因子又可进一步作用于胶质细胞,诱发炎症
风暴,从而触发抑郁的发生。非侵入物理疗法——630 nm红光照射可以激活甲醛脱氢酶(FDH)
而降解甲醛,减少中脑炎症因子,改善抑郁的行为症状。因此,无创的红光疗法可能是治疗抑郁
的一种新策略。
(赵丹睿,张凤吉,刘懿莹,吴一箐,赵夯,廖海康,潘文浩,程建华,童志前. 非侵入物理疗法——红光
照射改善脂多糖诱发小鼠抑郁样行为,本期第1664~1676 页)
Cover Story:Objective The unclear mechanism of depression occurrence and the undesired clinical efficacy of drugs are the difficult problems all over the world. Previous studies have found that gaseous formaldehyde (FA) exposure or intraperitoneal injection of FA can directly induce depression-like behaviors in mice. Whether endogenous FA leads to depression is unclear. This study was to explore whether lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces depression-like behaviors in mice by stimulating endogenous FA generation, and to observe whether non-invasive physical therapy——630 nm red light irradiation can activate FA dehydrogenase and degrade FA, thereby attenuate depression-like behaviors in mice.Methods Male adult C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into: (1) control group, intraperitoneal injection of phosphate buffered saline (PBS); (2) depression model group, intraperitoneal injection of LPS at a concentration gradient; (3) red light intervention group, these mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS and treated with 630 nm red light irradiation. The depression-like behaviors of mice were evaluated by open field test, sucrose preference test, tail suspension test and forced swimming test. The concentration and distribution of FA in brain tissue of mice were detected by FA fluorescence (Na-FA, specific FA fluorescent probe) quantitative method and whole brain FA fluorescence imaging. The concentrations of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 and semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) were detected by ELISA.Results One hour after acute injection of LPS, FA accumulated rapidly in the whole brain, especially in the midbrain. With the increase of IL-1β and TNF-α content; 24-hour depression-like behaviors, for example, open field total movement distance, central area movement time (distance) decreased significantly; the total immobility time of tail suspension test and forced swimming test were increased. However, 630 nm red light treatment significantly attenuated LPS-induced depression-like behavior in mice accompanied by a decrease in midbrain inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α.Conclusion The accumulation of FA in the midbrain is an initiating factor for depression, stimulating a large release of inflammatory factors and leading to depression-like behaviors. However, red light irradiation can scavenge FA and reduce neuroinflammation. It is a promising new strategy for non-invasive treatment of depression.
|
综述与专论
研究报告
技术与方法
科教融合
|
|