2016年第43卷第2期目录
| |
|
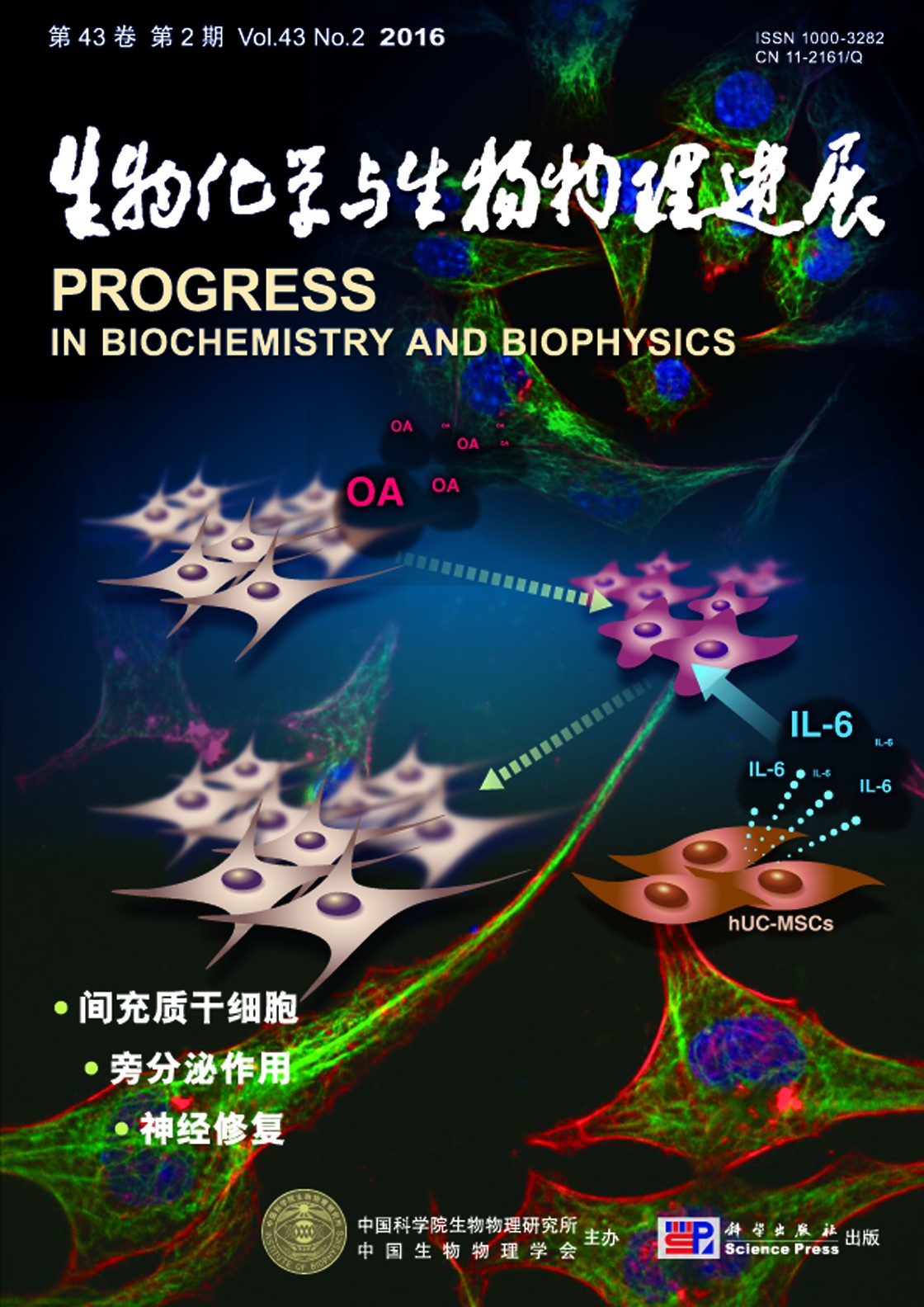
封面故事:大量文献报道和临床试验表示,人脐带来源的间充质干细胞(hUC-MSCs)对包括阿尔茨海默病(AD)在内的多种神经退行性疾病有治疗作用,尤其是其强大的旁分泌作用,在各种疾病的治疗研究中不容忽视.那么其旁分泌作用对AD相关的神经细胞损伤是否也有治疗或修复作用,这种作用又有怎样的作用机理呢?经过文献调研、实验框架搭建和实验数据获取,裴雪涛研究组发现,hUC-MSCs的分泌因子对经典的AD体外模型的受损细胞有明显的修复作用,并且IL-6作为hUC-MSCs重要的分泌因子,参与介导了这种修复作用.这一研究在体外模型的基础上,证实了hUC-MSCs对AD有治疗作用,肯定了hUC-MSCs强大的旁分泌作用,证实了其分泌因子对受损神经细胞的修复作用,并揭示了这种修复作用由其分泌的IL-6所介导.
(翟晶磊,曹 宁,岳 文,贾雅丽,裴雪涛. 人脐带间充质干细胞通过分泌IL?鄄6介导冈田酸对SH?鄄SY5Y细胞毒性的保护作用,本期第141~149页)
Cover Story:Alzheimer's disease (AD) is currently an incurable neurodegenerative disease, which is the most common cause of dementia worldwide. AD is also a progressive disorder, pathologically characterized by extracellular amyloid beta plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). NFTs consist of paired helical filaments of microtubule-associated tau protein that is hyperphosphorylated and the density of tau tangles correlates well with regional and global aspects of AD-associated cognitive dysfunction. Furthermore, the established toxic role of tau in certain genetic forms of frontotemporal dementia strongly suggests that tau aggregation may result in a toxic gain-of-function leading to the AD-associated neurodegeneration. Thus, there is a growing interest in discovering novel compounds that will help in reducing the deleterious accumulation of tau protein tangles in the AD brain. Stem cells treatment open a gate to this which many drugs show hard to control the disease progression or enhance the patients' consideration function. hUC-MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human Wharton's jelly of unbilical cord), emphasized by its powerful paracrine, great function of multi-directional differentiation and east to isolate, have been confirmed effective to many nervous system disease including AD. But the treatment mechanism was still unknown. Along with the studies of secreted factors by hUC-MSCs, the paracrine function of the adult stem cells attracted us to answer this treatment mechanism from those star factors. Here, we set up the AD model in vitro by okadaic acid (OA), and demonstrate that IL-6 maybe the key protein to effect the recovery function of hUC-MSCs to protect the injured cells.
|
综述与专论
研究报告
技术与方法
新技术讲座
|
|