2021年第48卷第11期目录
| |
|
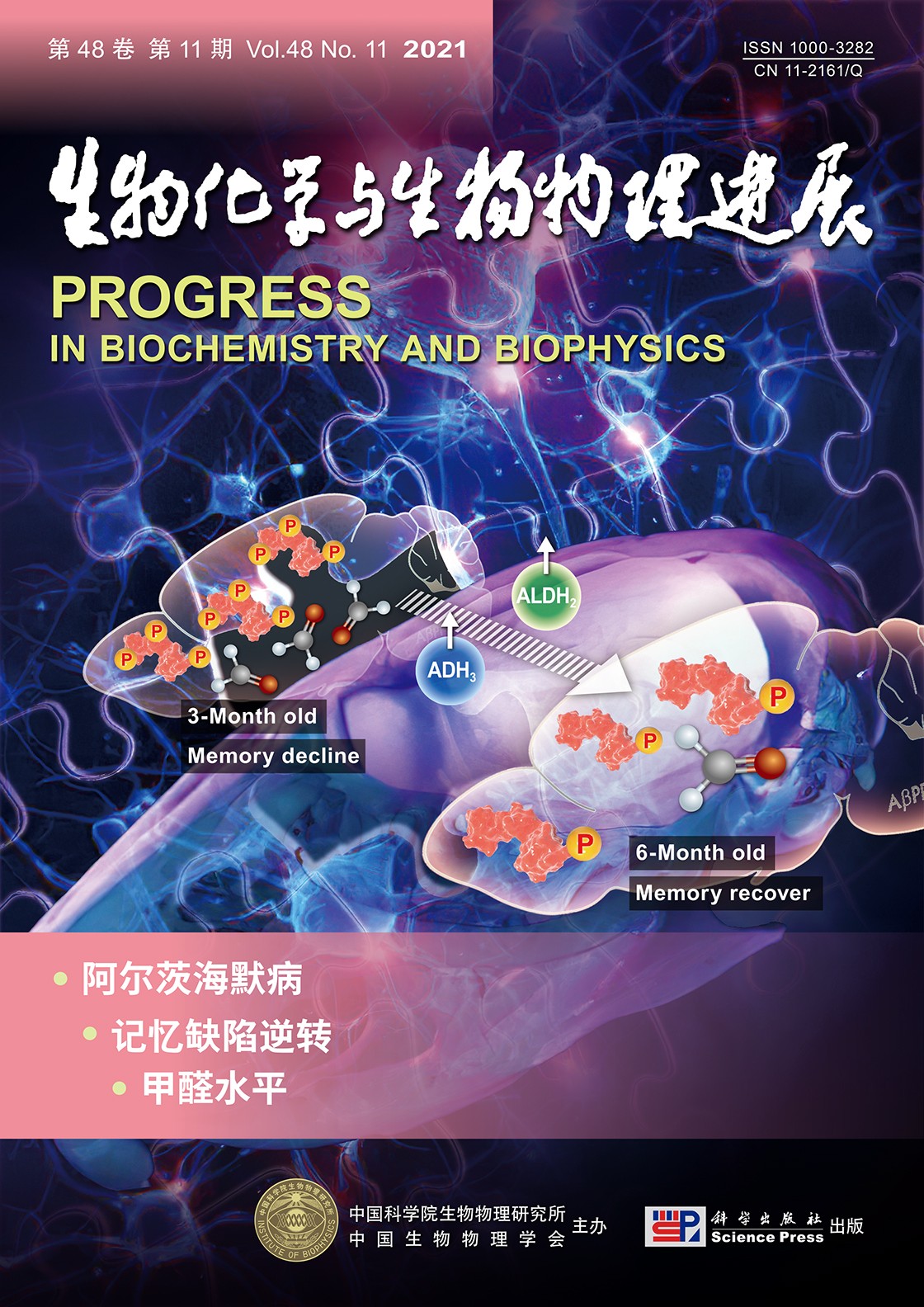
封面故事:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ) 沉积形成斑块是阿尔茨海默病(AD) 的病理标志之一. 以β淀粉样
前体蛋白(AβPP) 为基础的转基因小鼠模型表现出斑块形成加速和记忆损伤. 然而,在一些模型
中,记忆丧失与斑块形成的相关性较低. 赫荣乔实验室近期报道了AD患者和动物模型的认知障碍
与其体内甲醛(FA) 水平具有较强的相关性. 该实验室的进一步研究发现,AβPPLon/Swe<.sup>转基因小鼠
在3月龄表现出记忆缺陷,并伴有甲醛水平增高和tau过度磷酸化. 腹腔注射甲醛清除剂白藜芦醇可
以降低脑内甲醛水平和tau蛋白的磷酸化,恢复小鼠的记忆. 6月龄小鼠甲醛水平和记忆恢复正常,
同时伴有甲醛降解酶ALDH2和ADH3表达上调. 总之,AβPPLon/Swe转基因小鼠的记忆损害与恢复与其
脑甲醛水平显著相关,该发现可能为揭示阿尔茨海默病的发病机制研究提供了新视角.
(卢静,何欢,苗君叶,朱岩,李婷,陈茜茜,童志前,赫荣乔,刘缨. AβPPLon/Swe转基因小鼠记
忆缺陷逆转与甲醛水平降低相关,本期第1337~1347 页)
Cover Story:The formation of plaques by the deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) in the brain is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Transgenic mouse models based on amyloid- β precursor protein (AβPP) exhibited accelerated plaque formation and memory
impairment. However, in some models, the correlation between memory loss and plaque formation is poor. Our lab has recently
found a strong correlation between formaldehyde levels and cognitive impairment in AD patients and animal models. In the present
study, we found that working memory was inversely correlated with formaldehyde levels in AβPPLon/Swe transgenic mice, which
showed memory deficiency at 3 months of age but normal memory at 6 months. Impaired memory in 3-month-old mice was
accompanied by higher levels of formaldehyde and hyperphosphorylated tau than controls. Administration of resveratrol, which is a
formaldehyde scavenger, rescued the cognitive deficits in these mice by reducing formaldehyde levels and attenuating tau
hyperphosphorylation. With increased expression of formaldehyde catalytic enzymes such as aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2)
and alcohol dehydrogenase III (ADH3), 6-month-old AβPPLon/Swe mice displayed similar levels of formaldehyde and working memory
as controls. We discovered that brain formaldehyde levels were significantly associated with the progression of memory deficit in
AβPPLon/Swe transgenic mice, and that recovery of memory was associated with formaldehyde reduction. Our findings provide valuable
insights into the underlying mechanisms of AD.
|
综述与专论
研究报告
技术与方法
Letter to Editor
|
|