2016年第43卷第11期目录
| |
|
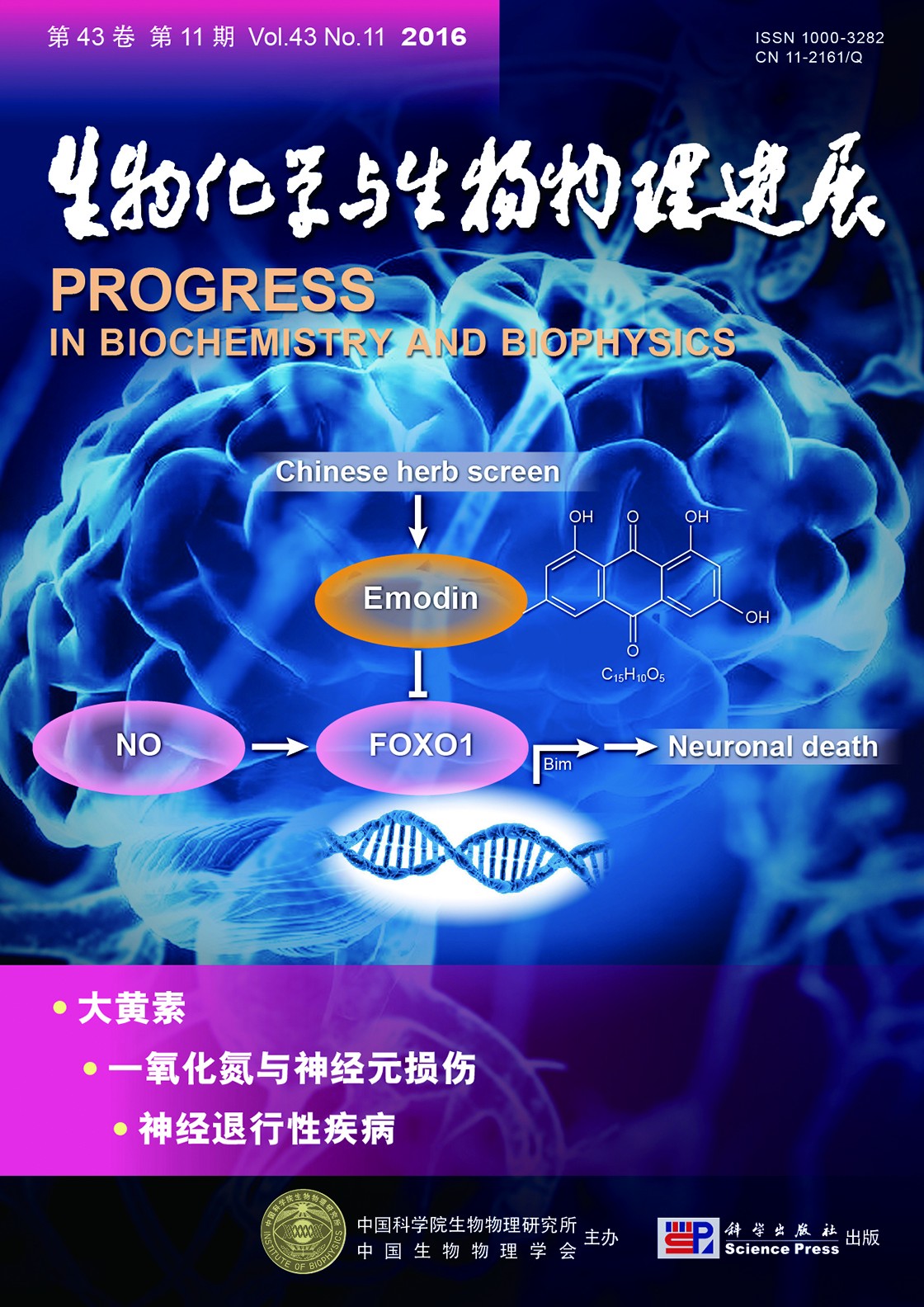
封面故事:氧化应激与阿尔茨海默病等神经退行性疾病的致病过程密切相关,但其具体的调节通路还不清楚.转录因子FOXO1在调控神经细胞凋亡中具有重要作用.陈素领等发现一氧化氮(NO)可显著激活FOXO1的转录活性并促进其下游促凋亡基因FasL,Bim的转录表达,进而诱导神经元死亡.这提示FOXO1可以作为一个很好的药物靶点,通过筛选抑制FOXO1活性的药物来缓解氧化应激导致的神经元损伤.陈素领等进而从大量中药化合物中筛选出大黄素,发现它可通过降低FOXO1的转录水平以及蛋白水平,缓解NO所诱导的神经元凋亡.本研究揭示了NO自由基诱导神经元损伤的新机制,以及大黄素的抗氧化作用对神经元凋亡的保护效应,为阿尔茨海默病等神经退行性疾病的防治等研究提供了新的思路和依据.
(陈素领,周杰超,张 杰,庄江兴,刘 娅.大黄素通过抑制FOXO1活性减轻NO对神经细胞的损伤,本期第1076~1085页)
Cover Story:Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and NO free radicals generated from oxidative stress play an important role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disease and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Excessive NO production can cause free radical damage and induce neuron death. As one of the traditional Chinese medicine, Emodin have valuable and widely clinical applications. Recently, Emodin has been reported to have antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antibacterial, anti-inflamatory functions etc. FOXO1 is a vital member of the Forkhead family of transcription factors known to regulate the transcription of genes involved in cell cycle arrest, DNA repair in response to oxidative stress or apoptosis. However, it is unclear how the NO effect on FOXO1. In this study, we observed vital role of FOXO1 dependent transcriptional activation on neuronal death in response to Nitric oxide over-production. We found that NO donor GSNO or L-Arginine significantly increased the FOXO1 transcriptional activity, which induce the FOXO1 downstream proapoptotic genes (FasL, Bim) expression and finally induce neuronal death. In addition, we screen natural Chinese herb extracts targets to regulating FOXO1 activity. Emodin shows dramatically effect in suppression of FOXO1 transcription activity and protein levels. What’s more, Emodin can attenuate neuronal death induced by L-Arg. The current study first demonstrate that Nitric Oxide could regulate FOXO1 transcriptional activity to damage neuronal cell, which will benefit to deep understanding the neurotoxicity of NO free radical. Secondly, by Chinese herb extracts and antioxidants screen, we identified Emodin as one FOXO1 activity modulator which can attenuate neurotoxicity induced by NO. The current study will also provide a new insight for explaining the mechanisms of pathology of neurodegenerative disease and neuroprotective effects of Emodin.
|
综述与专论
研究报告
技术与方法
新技术讲座
|
|